top of page
Geometry & Trigonometry

ANGLES
Example 1) How to use a protractor to measure angles
Step 1) Find the vertex and put the mid-point of the protractor there.


Step 2) Find where the angle arm reaches

Types of Angles:
Types of Angles
Right / 90* angle
Acute Angle
(less than 90*)

Obtuse Angle
(Greater than 90*)

Reflex Angle
Exterior Angle

Practice
Practice PDFs available for download:

POLYGONS
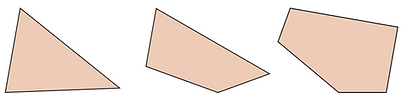
Polygon: a multiple-sided shape
-
a closed shape
-
sides are stright line segments
-
only 2 sides meet at a vertex
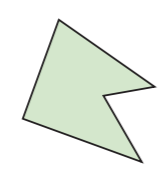
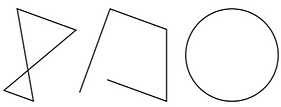
Non-Polygons:
Regular Polygon: all sides are equal and all angles equal:

Irregular Polygon: Does not have all sides equal and all angles equal:
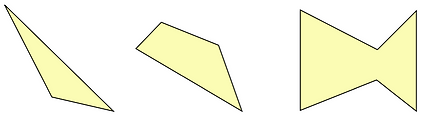
Convex Polygon: Has all angles less than 180*:
Concave Polygon: Has at least one angle greater than 180*:

Perimeter of Polygons
Perimeter
Perimeter: is the distance around a polygon
P = sum of all side lengths

8cm
6cm
Perimeter = 8 + 7 + 6
= 21cm
7cm
Practice
Practice PDFs available for download:

AREA
Area of Rectangles
Area of Rect
Area = (Length) x (width)
Formula:
Example 1) Calculate the area of the following rectangle:
Area = 3 x 9
= 27m
2
3m
9m
Here we say, "twenty-seven meters squared."
We say squared because it lets everyone know our answer is 2 dimensional (both length & width) to cover space
Practice
Practice PDFs available for download:
Area of Triangles
Example 1) Calculate the area of the following triangle:
Formula:
A =
Base x Height
2

6cm
10cm
8cm
Step One: Fill in the formula with what you know; base is 8cm, height is 6cm
8cm x 6cm
2
Step Two: Complete the top part of the equation (8*6)
8cm x 6cm
= 48cm
Step Three: Complete the top part of the equation (8*6)
48cm
2
= 24cm
2
Practice
Practice PDFs available for download:
Surface Area
1) Rectangular Prisms
SA of rect, tri & Cyl
Example) Find the surface area of this rectangular prism:

Step 1) Draw the net of the shape:

Step 2) Notice there are 3 pairs of congruent rectangles within the prism:
-
A&D are congruent rectangles
-
B&E are congruent rectangles
-
D&F are congruent rectangles
-
This means you can solve for the surface area a shorter way:
Surface area = 2 x (area of rectangle A)
+ 2 x (area of rectangle B)
+ 2 x (area of rectangle C)
Step 3) Solve area of each rectangle:
Rectangles A&D = 2(3 x 5) = 30cm
Rectangles B&E = 2(8 x 3) = 48cm
Rectangles C&F = 2(8 x 5) = 80cm


Step 4) Add up areas of all the rectangles calculated in step 3:
A&D: 30cm
B&E: 48cm
+ C&F: 80cm
2
2
2

We say the surface area of the rectangular prism is:
158cm
2
2) Surface Area of Triangular Prisms
Example) Find the surface area of this triangular prism:

Step 1) Draw the net of the shape:

Step 2) Notice some sides of the triangular prism are congruent:
-
A&C are congruent rectangles
-
D&E are congruent triangles
-
B does not have any congruent shapes
-
This means you can solve for the surface area a shorter way:
Surface area = 2 x (area of rectangle A)
+ 2 x (area of triangle D)
+ area of rectangle B

Step 3) Recall the formula for area of a triangle and solve area of each triangle & rectangle:
Rectangles A&C = 2(20 x 9) = 360cm
Triangles D&E = 2(15 x 5) = 75cm
Rectangle B = (15 x 20) = 300cm
2

Formula for area of a triangle:
2
A =
Base x Height

Step 4) Add up areas of all the shapes calculated in step 3:
A&C: 360cm
D&E: 75cm
+ B: 300cm
2
2
2
735cm
2
We say the surface area of the triangular prism is:
3) Surface Area of Cylinders
Example) Find the surface area of this cylinder:

Step 1) Draw the net of the shape:
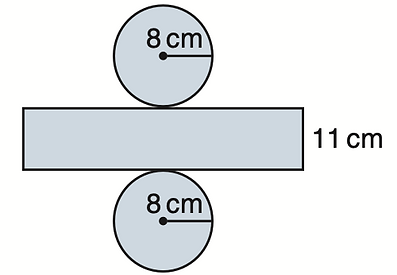
Step 2) Notice some sides of the cylinder are congruent:
-
Two circles
-
One rectangle
-
This means you can solve for the surface area a shorter way:
Surface area = 2 x (area of one circle)
+ area of the rectangle

Step 3) Recall the formula for area of a circle and solve area of each circle & rectangle:
Circles = π x 8
2

= 201.06 x 2circles
= 402.12
Area of Rectangle = circumference x height
= 2 x π x 8 x 11
Formula for area of a circle:
A =
π x radius
2
Formula for circumference of a circle:
C =
2πr
= 552.92

Step 4) Add up areas of all the shapes calculated in step 3:
Two Circles: 402.12cm
One Rectangle: + 552.92cm
2
2
955.04cm
2
We say the surface area of the cylinder is:

VOLUME
Volume of Rectangular Prisms
Volume is the three dimensional space a figure takes up.
Calculated in cubic units
Length x Width x Height
Formula:
Example 1) Calculate the volume of the following rectangular prism:
2

V = l x w x h
= 11cm x 4cm x 5cm
= 44cm x 5cm
= 220cm
3
Here we say, "two-hundred twenty centimeters cubed."
We say Cubed because it lets everyone know our answer is 3 dimensional (length & width & height) to fill 3D space
Practice
Practice PDFs available for download:
Volume of Triangular Prisms
Example) Find the volume of this triangular prism:
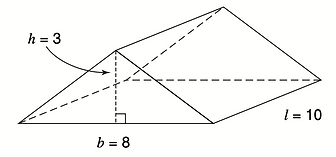
Base Area x Length
Volume Formula:
2
Step 1) Solve the base area of the shape:
Recall the formula for the area of a triangle & Solve.
Area of Triangle = 8 x 3 = 12cm
2
Formula for area of a triangle:
2
A =
Base x Height

Step 2) Multiply the base by the length of the shape:
Base x Height = 12cm x 10cm
2
= 120cm
3
We say the volume of the triangular prism is:
**Note the exponent is "3" indicating a "cubed unit" and a measure of volume not surface area.
Volume of Cylinders

Base Area x Length
Volume Formula:
Volume of a cylinder is V = base area x height
= area of a circle x height
= πr x h
2
So, a formula for the volume of a cylinder is V = πr x h,
where "r" is the radius of its base, and "h" is its height
2

Example) Solve the volume of this cylinder:
Solution:
Volume of a cylinder = base area x height
= 154 x 24
= 3696cm
3



TRIGONOMETRY
Types of Triangles
6 Types of Triangles:
Based on Angles:
Right Triangle: one angle is 90 degrees
Acute Triangle: All angles are less than 90 degrees
Obtuse Triangle: One angle is greater than 90 degrees
Based on Side Lengths:
Equilateral Triangle: all sides are equal & all angles are equal
Isosceles Triangle: 2 sides are equal & 2 angles are equal
Scalene Triangle: no sides nor angles are equal

Practice
Practice PDFs available for download:
Pythagorean Theory


Notice a relationship between the area of each square attached to the triangle: 25 = 9 + 16
In a right triangle, the area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the legs.
This relationship is called the Pythagorean Theory
The formula is written: a + b = c
2
2
2
Where a is one leg, b is one leg, and c is the hypotenuse of a triangle.
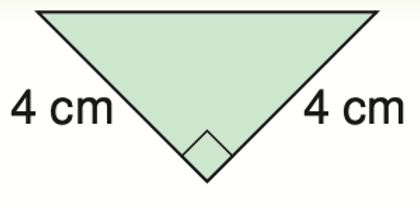
Example) Find the length of the hypotenuse
C
Step 1) Use the Pythagorean Theory: a + b = c
2
2
2
4 + 4 = c
2
2
2
16 + 16 = c
2
32 = c
2

The area of the square on the hypotenuse is 32.
So, the side length of the square is: c =
Step 2) Use a calculator. Solve for
C = 5.6569

So, the hypotenuse is approximately 5.7cm.
The Tangent Ratio


We name sides of right triangles in relation to one of its acute angles.
Example 1) Using the Tangent Ration to solve ANGLES

Determine the angles of G and J.
Step 1) Write the Tan Ratio Formula:
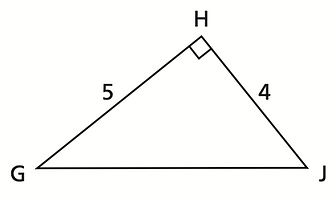



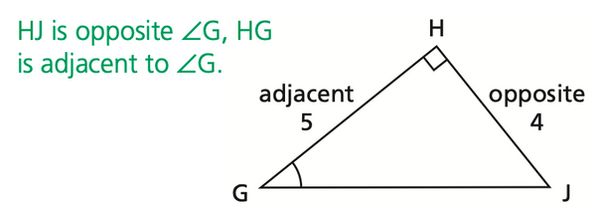
Step 2) Use a calculator. = 0.8
4
5

Type tan (0.8) into your calculator
=38.7
-1
Since all triangles' interior angles add up to 180°, we can subtract ∠H (90°) and ∠G (38.7°) from 180° to find the last angle.
180° - (90° + 38.7°)
128.7°
180° - 128.7° = 51.3°

So, ∠G = 38.7°
and ∠J = 51.3°
Example 2) Using the Tangent Ration to solve Opposite SIDE LENGTHS

Determine the length of AB.
Step 1) Write the Tan Ratio Formula:
Tan (angle) = ----------------------------
length of opposite
length of adjacent


Given ∠C (30°), the opposite length is side AB
and the adjacent length is side BC



Step 2) Solve this equation for AB.

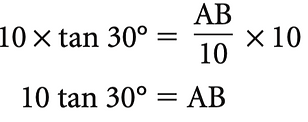
Multiply both sides by 10.
we write: 10 x tan(30°)
Step 3) Type 10 x tan(30°) in your calculator
=5.77

So, AB is approximately 5.8cm long
When to use Sine, Cosine, Tangent
The Primary Trigonometric Ratios


How do they work?
The values of the sine, and cosine compare the side lengths of a triangle.
For example, if Sin A = 0.5, that means the opposite side length to ∠A is 0.5 times the length of the hypotenuse:
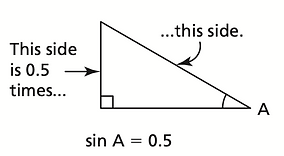
If Cos A = 0.7, that means the adjacent side length to ∠A is 0.7 times the length of the hypotenuse:

Example 1) Using the Sine Ratio to solve an Angle

a) Identify the side ∠D and the side adjacent to ∠D.
b) Determine ∠D using the Sine Ratio.
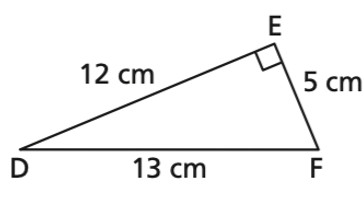
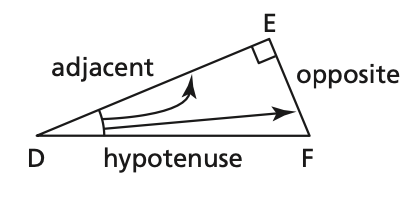
Step 1) Identify the hypotenuse, adjacent and opposite sides of the triangle:
-
DF is the Hypotenuse
-
EF is the Opposite of ∠D
-
DE is the Adjacent of ∠D
Step 2) Solve for Sin D using the Sine Ratio:

Sin D = 0.38
EF is opposite ∠D
DF is the hypotenuse
Use a calculator, use sin to determine its measurement of ∠D in degrees
-1
Type Sin (0.38) into your calculator
=22.3
-1
So, ∠D = 22.3°
Example 2) Using the Cosine Ratio to solve for an Angle

a) Determine the measure of ∠G
Step 1) Identify the hypotenuse, adjacent and opposite sides of the triangle:
-
GH is the Hypotenuse
-
KH is the Opposite of ∠G
-
GK is the Adjacent of ∠G


GK is adjacent ∠G
GH is the hypotenuse
Cos G = 0.428
Use a calculator, use cos to determine its measurement of ∠G in degrees
-1
Type Cos (0.428) into your calculator
=64.6
-1
So, ∠G = 64.6°
Trigonometry Finale
bottom of page
